Social Emotional Learning is the key to lifelong success

What is SEL?
Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) is the process of developing emotional intelligence skills that are crucial for success in daily life.
Core Competencies
STRUT Learning is in full alignment with these competencies. However, we further added a 6th component, motivation, which is critical for education, technology, and students. In addition, we have broken up the 6 competencies into 18 sub-competencies for a deeper analysis and understanding.
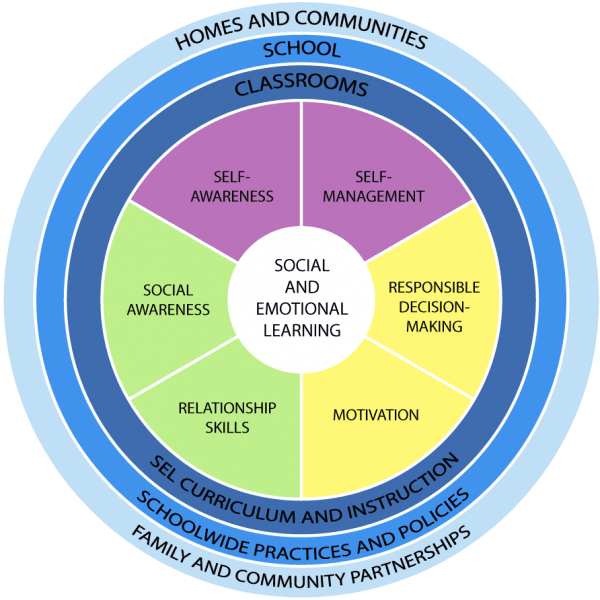
SOCIAL AND EMOTIONAL LEARNING (SEL) COMPETENCIES
SELF-AWARENESS
The abilities to understand one’s own emotions, thoughts and values and how they influence behaviors across contexts.
- Emotional Awareness – The ability to make sense of one’s own emotions as well as the emotions of others.
- Self-Perception – The ideas and thoughts one has about themselves.
- Optimistic Outlook – Positivity and hope with regards to futuristic outcomes.
SELF-MANAGEMENT
The abilities to manage one’s own emotions, thoughts and behaviors effectively in different situations and to achieve goals and aspirations.
- Internal regulation- The ability to regulate one’s own emotions and thoughts and take control over how they are managed.
- Behavior control- The ability to regulate one’s own behaviors.
- Goal pursuance- The desire to achieve specific outcomes and the willingness to take steps to reach those goals.
SOCIAL AWARENESS
The abilities to understand the perspectives of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds, cultures and contexts.
- Appreciating social & environmental diversity- The ability to appreciate diverse perspectives, even when they differ from one’s own.
- Adaptive behavior- The ability to adapt to new environments and situations with the willingness to learn and explore.
- Resource and support recognition- The ability to recognize one’s support networks and utilize them as needed.
RELATIONSHIP SKILLS
The abilities to establish and maintain healthy and supportive relationships and to effectively navigate settings with diverse individuals and groups.
- Communication- The ability to convey information as necessary in a clear, respectful, and kind manner.
- Social engagement- The amount that one interacts with communities and society as a whole through active participation, conversation, and connection.
- Interdependence- One’s ability to depend on others while still maintaining a strong sense of self.
RESPONSIBLE DECISION MAKING
The abilities to make caring and constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions across diverse situations.
- Constructive thinking- The ability to think about one’s choices, ensuring maximum personal growth and minimizing friction with others.
- Consequence evaluation- One’s ability to consider potential consequences of all possible decisions prior to making a decision.
- Respect for self and others- The ability and awareness to treat oneself and others with kindness and compassion.
MOTIVATION
The desire to act in order for certain goals to be achieved.
- Enthusiasm- A deep interest and excitement in what is being experienced.
- Initiative- The ability to take control of situations in order to enhance one’s situation.
- Resilience- One’s ability to cope with and handle difficult situations and ultimately find new pathways to move themselves forward.
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL). (n.d.). What Are the Core Competence Areas and Where are they Promoted?Retrieved from https://casel.org/sel-framework/
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL). (n.d.). Overview of SEL. Retrieved from https://casel.org/overview-sel/
Weissberg, R. P., Durlak, J. A., Domitrovich, C. E., & Gullotta, T. P. (Eds.). (2015). Social and emotional learning: Past, present, and future. In J. A. Durlak, C. E.Domitrovich, R. P. Weissberg, & T. P. Gullotta (Eds.), Handbook of social and emotional learning: Research and practice (pp. 3-19). New York, NY, US: Guilford Press.

